Eco-Friendly Home Design: Save Up to 20% on Energy Bills This Winter
Eco-friendly home design offers practical solutions to significantly reduce winter energy consumption, potentially saving homeowners up to 20% on their utility bills through sustainable practices and smart investments in energy-efficient technologies.

Advertisement
Eco-friendly home design offers practical solutions to significantly reduce winter energy consumption, potentially saving homeowners up to 20% on their utility bills through sustainable practices and smart investments in energy-efficient technologies.
As winter approaches, many homeowners in the United States begin to brace for the inevitable rise in heating costs. However, by embracing eco-friendly home design principles, you can transform your residence into a haven of warmth and efficiency, potentially saving up to 20% on your energy bills this season. This approach isn’t just about cutting costs; it’s about creating a healthier, more sustainable living environment for your family.
Advertisement
Understanding the Core of Eco-Friendly Home Design
Eco-friendly home design is more than just a trend; it’s a holistic philosophy focused on minimizing a home’s environmental impact while maximizing its efficiency and comfort. This involves thoughtful planning, material selection, and system integration to reduce energy consumption, conserve resources, and promote indoor air quality.
The core tenets revolve around passive design strategies, renewable energy integration, and the use of sustainable, non-toxic materials. By understanding these fundamentals, homeowners can make informed decisions that benefit both their wallets and the planet.
Advertisement
Passive Design Principles for Winter Warmth
Passive design harnesses natural energy sources, primarily the sun, to heat and light a home. This reduces the reliance on mechanical systems, leading to significant energy savings. Proper orientation, window placement, and thermal mass are crucial components.
- Solar Orientation: Positioning your home to maximize southern exposure allows for ample sunlight penetration during winter, naturally warming interior spaces.
- Window Selection: High-performance, low-emissivity (Low-E) windows prevent heat from escaping while allowing sunlight in, acting as an insulator.
- Thermal Mass: Materials like concrete, stone, or water can absorb and store heat during the day, slowly releasing it at night, maintaining a stable indoor temperature.
Implementing passive design from the outset of a new build or during a major renovation can yield substantial, long-term energy savings. Even in existing homes, strategic additions like heavy drapes or exterior shading can contribute.
Sustainable Materials and Their Impact
The choice of building materials plays a significant role in a home’s eco-friendliness. Opting for sustainably sourced, recycled, or rapidly renewable materials reduces the carbon footprint associated with construction and renovation.
For instance, bamboo flooring is a fast-growing, renewable resource, while reclaimed wood reduces demand for new timber. Insulation made from recycled denim or cellulose offers excellent thermal performance with minimal environmental impact. These materials often contribute to better indoor air quality by reducing volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other harmful chemicals.
The impact of material selection extends beyond initial construction. Durable, long-lasting materials reduce the need for frequent replacements, further minimizing waste and resource consumption over the home’s lifespan.
Ultimately, eco-friendly home design integrates environmental responsibility with practical savings. By focusing on these fundamental principles, homeowners can create a more comfortable, efficient, and sustainable living space, especially crucial when facing colder months and higher energy demands.
Maximizing Insulation and Air Sealing for Peak Efficiency
One of the most effective ways to achieve substantial energy savings during winter is by ensuring your home’s thermal envelope is robust. This means maximizing insulation and meticulously sealing air leaks. A well-insulated and sealed home retains heat more effectively, reducing the workload on your heating system and translating directly into lower energy bills.
Many older homes, in particular, suffer from inadequate insulation and numerous hidden air leaks, which act as energy vampires, constantly siphoning warm air out and cold air in. Addressing these issues is often the first and most impactful step towards an eco-friendly and energy-efficient home.
Understanding Your Home’s Thermal Envelope
Your home’s thermal envelope is essentially the boundary between conditioned (heated or cooled) and unconditioned spaces. This includes your walls, ceilings, floors, windows, and doors. Any breach in this envelope can lead to significant heat loss. Identifying and addressing these weak points is paramount.
- Attic Insulation: Often the easiest and most cost-effective place to add insulation. A well-insulated attic prevents heat from rising and escaping through the roof.
- Wall Insulation: While more challenging to retrofit, improving wall insulation can dramatically reduce heat transfer, especially in older homes with hollow walls.
- Floor Insulation: Insulating floors, especially those above unheated basements, crawl spaces, or garages, prevents cold air from seeping upwards.
Different types of insulation offer varying R-values (a measure of thermal resistance) and installation methods. Consulting with an energy auditor can help determine the most effective insulation strategy for your specific home.
The Critical Role of Air Sealing
Insulation alone isn’t enough; air leaks can undermine even the best insulation. Gaps and cracks around windows, doors, electrical outlets, plumbing penetrations, and attic hatches allow conditioned air to escape and unconditioned air to infiltrate. Sealing these leaks is a low-cost, high-impact measure.
Common air sealing materials include caulk for smaller gaps, weatherstripping for movable components like windows and doors, and expanding foam for larger openings. A professional energy audit often includes a blower door test, which can pinpoint exactly where your home is leaking air, allowing for targeted sealing efforts.
By preventing drafts and uncontrolled air exchange, air sealing not only saves energy but also improves indoor comfort by eliminating cold spots and reducing the entry of dust and allergens. It works in tandem with insulation to create a truly efficient thermal barrier.
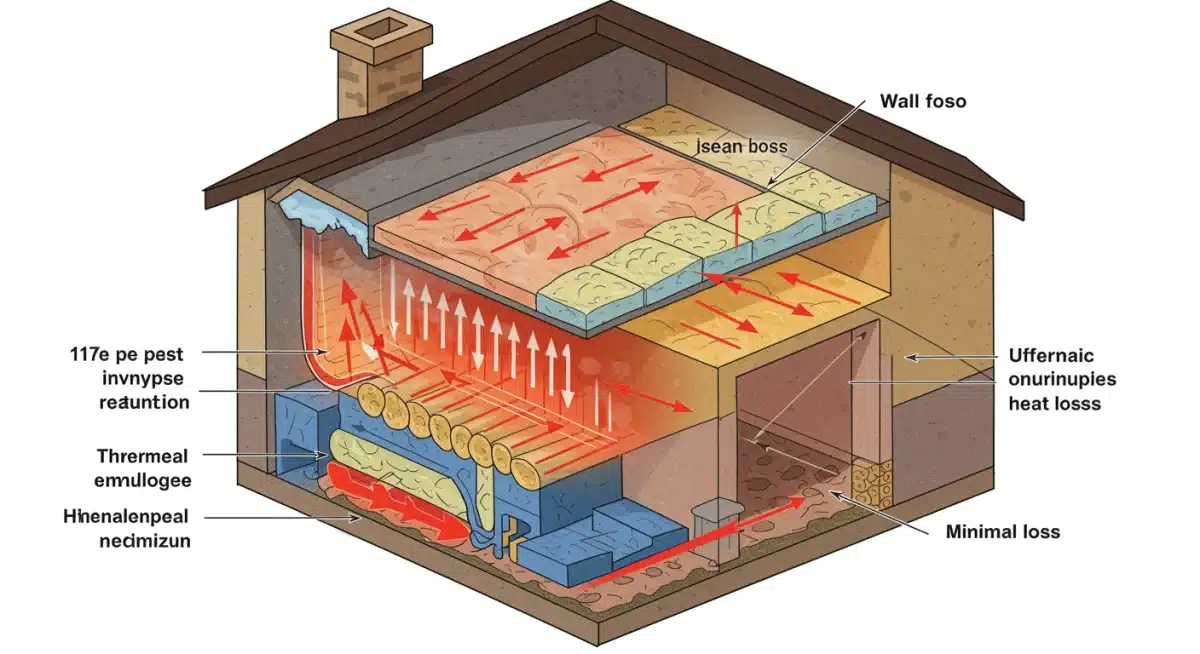
Investing in superior insulation and thorough air sealing provides immediate and tangible benefits, making your home significantly more comfortable and reducing your winter energy bills. These measures are foundational to any serious eco-friendly home design strategy aimed at long-term energy savings.
Smart Heating Solutions and Renewable Energy Integration
Beyond the passive measures of insulation and air sealing, incorporating smart heating solutions and exploring renewable energy options can further propel your home into the realm of eco-friendliness and significant energy savings. Modern technology offers sophisticated ways to manage heating more efficiently, while renewable sources provide sustainable alternatives to traditional fossil fuels.
These active strategies, when combined with passive design, create a powerful synergy that maximizes comfort while minimizing environmental impact and operating costs. The goal is to heat your home effectively with the least amount of energy possible, ideally from clean sources.
Embracing Smart Thermostats and Zoned Heating
Smart thermostats are a cornerstone of modern energy management. These devices learn your family’s habits, optimize heating schedules, and can be controlled remotely via smartphone apps. This level of control ensures your home is only heated when and where it’s needed, preventing wasted energy.
- Adaptive Scheduling: Automatically adjusts temperature based on occupancy patterns.
- Remote Access: Control your heating from anywhere, ensuring you don’t heat an empty home.
- Energy Reporting: Provides insights into your energy usage, helping you identify areas for further savings.
Zoned heating systems take efficiency a step further by allowing different areas (zones) of your home to be heated independently. Why heat the entire house when only a few rooms are occupied? This targeted approach can lead to substantial energy reductions, especially in larger homes.
Exploring High-Efficiency Heating Systems
For homes relying on traditional heating, upgrading to a high-efficiency furnace or boiler can offer significant savings. Modern systems are designed to convert a higher percentage of fuel into usable heat, reducing waste.
Heat pumps, particularly air-source or geothermal heat pumps, are another excellent eco-friendly option. They don’t generate heat; instead, they move heat from one place to another. In winter, they extract heat from the outside air or ground and transfer it indoors, a highly efficient process.
While the initial investment for these systems can be higher, the long-term energy savings and reduced environmental footprint often justify the cost, with many government incentives and rebates available to offset upfront expenses.

Integrating renewable energy sources, such as solar panels for electricity generation or solar thermal systems for water heating, can further reduce your reliance on the grid and fossil fuels. These systems not only lower your energy bills but also increase your home’s energy independence and value, making your home truly eco-friendly and cutting-edge in its energy management.
Water Conservation and Efficient Appliances
While heating often dominates winter energy bills, water heating also contributes significantly to overall energy consumption. An eco-friendly home design extends beyond space heating to encompass all aspects of resource use, including water. By conserving water and utilizing energy-efficient appliances, homeowners can achieve additional savings and further reduce their environmental footprint.
Every gallon of hot water used requires energy to heat it, so reducing hot water consumption directly impacts energy bills. Similarly, choosing appliances that perform their tasks using less energy and water contributes to a more sustainable household.
Strategies for Reducing Hot Water Use
Simple behavioral changes and smart fixtures can dramatically cut down on hot water usage. These small adjustments add up to considerable savings over time, especially during colder months when hot showers and baths are more frequent.
- Low-Flow Fixtures: Installing low-flow showerheads and faucet aerators reduces the amount of hot water used without sacrificing pressure.
- Efficient Water Heaters: Consider tankless water heaters, which heat water on demand, or heat pump water heaters, which are significantly more efficient than traditional tank models.
- Insulate Pipes: Insulating hot water pipes prevents heat loss as water travels from the heater to the faucet, ensuring hot water arrives faster and stays hot longer.
Beyond these upgrades, conscious habits like taking shorter showers, washing clothes in cold water, and running dishwashers only when full can make a substantial difference in both water and energy consumption.
Investing in Energy-Efficient Appliances
Appliances account for a significant portion of household energy use. When it’s time to replace an old appliance, choosing an ENERGY STAR certified model is a smart eco-friendly decision. These products meet strict energy efficiency guidelines set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
Look for the ENERGY STAR label on refrigerators, dishwashers, washing machines, and other large appliances. While they may have a slightly higher upfront cost, the long-term energy savings often pay for themselves quickly, sometimes within just a few years.
For example, an ENERGY STAR certified refrigerator uses about 9% less energy than a non-certified model, while an ENERGY STAR washing machine uses about 25% less energy and 33% less water. These savings are cumulative and contribute significantly to a greener household budget and a reduced carbon footprint.
By integrating water conservation measures and opting for energy-efficient appliances, homeowners can create a more comprehensive eco-friendly home design that addresses multiple facets of energy and resource consumption, leading to a truly sustainable and cost-effective living environment.
Landscaping and Exterior Enhancements for Winter Efficiency
The exterior of your home, including your landscaping, plays a surprisingly significant role in its overall energy efficiency, especially during the winter months. Strategic planting and exterior enhancements can act as natural insulators and windbreaks, further reducing your heating load and contributing to your eco-friendly home design goals.
Many homeowners overlook the potential of their outdoor spaces to contribute to indoor comfort and energy savings. However, with thoughtful planning, your yard can become an integral part of your home’s thermal management strategy, working in harmony with your insulation and heating systems.
Strategic Planting for Windbreaks and Solar Gain
Deciduous trees planted on the south side of your home can provide shade in the summer, blocking harsh sunlight, and then shed their leaves in winter, allowing the sun’s warmth to penetrate your home. Evergreen trees, on the other hand, can be strategically planted on the north and northwest sides of your property to act as effective windbreaks.
- Evergreen Windbreaks: Dense evergreens can significantly reduce wind speeds around your home, minimizing heat loss due to infiltration and convection.
- Deciduous Solar Gain: Properly placed deciduous trees allow passive solar heating during winter, reducing the need for artificial heating.
- Shrubs and Hedges: Lower plantings close to the foundation can create a dead air space, providing an additional layer of insulation against cold winds.
When planning your landscaping, consider the mature size and shape of plants to ensure they fulfill their energy-saving function without obstructing views or creating unwanted shade.
Exterior Shading and Thermal Mass Elements
While often associated with summer cooling, certain exterior elements can also contribute to winter efficiency. Overhangs and awnings, for example, can be designed to block high summer sun while allowing lower winter sun to enter. This passive solar strategy is highly effective.
Additionally, incorporating thermal mass into your exterior design, such as stone walls or pathways that absorb and radiate heat, can help moderate outdoor temperatures around your home, indirectly impacting indoor comfort. Even paved areas can absorb solar radiation during the day and release it slowly, reducing the intensity of cold around your home’s perimeter.
Maintaining a well-designed exterior goes beyond aesthetics; it’s an actionable component of an eco-friendly home design that contributes to year-round energy savings. By intelligently using natural elements and structural features, you can significantly enhance your home’s winter performance and lower your heating costs.
The Economic and Environmental Benefits of Going Green
Adopting an eco-friendly home design offers a myriad of advantages that extend far beyond simply saving money on energy bills. While the prospect of cutting winter heating costs by up to 20% is certainly appealing, the economic and environmental benefits associated with sustainable living are much broader and more profound. This holistic approach positively impacts your finances, your health, and the planet.
Making conscious choices in how we build, renovate, and maintain our homes is a powerful way to contribute to a more sustainable future, while also creating a more comfortable and valuable asset for our families.
Long-Term Financial Savings and Increased Home Value
The most immediate and tangible benefit for many homeowners is the significant reduction in utility bills. By implementing energy-efficient measures, you lock in lower operating costs for your home for years to come. These savings can accumulate to thousands of dollars over the lifespan of your home, effectively providing a return on your initial investment.
- Lower Utility Bills: Direct savings on heating, cooling, electricity, and water.
- Government Incentives: Access to tax credits, rebates, and grants for energy-efficient upgrades.
- Increased Home Value: Eco-friendly homes are increasingly attractive to buyers, often commanding higher resale prices and selling faster.
Beyond direct savings, many states and federal programs offer incentives for homeowners who invest in renewable energy systems or energy-efficient upgrades. These financial aids can significantly reduce the upfront cost of going green, making it a more accessible option for many.
Positive Environmental Impact and Health Benefits
Reducing your home’s energy consumption directly translates to a smaller carbon footprint. Less reliance on fossil fuels means fewer greenhouse gas emissions, helping to combat climate change and preserve natural resources. This personal contribution to environmental stewardship is a powerful motivator for many.
Furthermore, eco-friendly homes often boast superior indoor air quality. By using non-toxic materials, improving ventilation, and reducing moisture buildup, these homes minimize exposure to allergens, pollutants, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). This leads to a healthier living environment, particularly beneficial for families with children or individuals with respiratory sensitivities.
The transition to an eco-friendly home design is an investment in both personal well-being and global sustainability. It’s about building a future where comfort, cost-effectiveness, and environmental responsibility coexist harmoniously, creating a legacy of responsible living for generations to come.
Making the Transition: Practical Steps and Considerations
Embarking on the journey to an eco-friendly home design might seem daunting, but it’s a transition that can be approached systematically, starting with small, manageable steps. The key is to prioritize interventions that offer the greatest impact for your budget and lifestyle, gradually transforming your home into an energy-saving haven. Understanding the process and potential challenges will empower you to make informed decisions and maximize your winter savings.
It’s not about doing everything at once, but rather about creating a strategic plan that aligns with your household’s needs and financial capabilities. Every step, no matter how small, contributes to the larger goal of a sustainable and efficient home.
Starting with an Energy Audit
The first and most crucial step in transitioning to an eco-friendly home is to conduct a professional energy audit. An energy auditor will assess your home’s current energy performance, identify areas of heat loss and inefficiency, and provide a detailed report with prioritized recommendations.
- Identify Problem Areas: Pinpoint exactly where your home is losing the most energy.
- Prioritize Investments: Receive tailored recommendations on which upgrades will yield the best return on investment.
- Quantify Potential Savings: Get an estimate of how much you can expect to save on your energy bills.
This audit acts as a roadmap, guiding your eco-friendly upgrades and ensuring that your efforts are focused on the most impactful interventions, whether it’s improving insulation, sealing drafts, or upgrading heating systems.
Phased Approach to Upgrades
You don’t need to overhaul your entire home at once. A phased approach allows you to spread out costs and integrate upgrades over time. Start with low-cost, high-impact measures like air sealing and adding attic insulation, then move on to more significant investments like window replacements or new heating systems.
Consider the lifespan of your existing systems. If your furnace is nearing the end of its life, planning to replace it with a high-efficiency model or a heat pump becomes a natural next step in your eco-friendly transition. Similarly, when replacing appliances, always opt for ENERGY STAR certified models.
Engaging with local contractors specializing in energy-efficient home improvements can provide valuable expertise and ensure proper installation. Look for certifications and positive reviews to ensure you’re working with reputable professionals.
By taking a measured and informed approach, the transition to an eco-friendly home design becomes an achievable and rewarding endeavor, leading to substantial energy savings and a more comfortable, sustainable living space for your family this winter and for many years to come.
| Key Eco-Friendly Action | Winter Energy Saving Impact |
|---|---|
| Maximize Insulation & Air Sealing | Significantly reduces heat loss through walls, attic, and gaps, cutting heating demand. |
| Install Smart Thermostats | Optimizes heating schedules and allows remote control, preventing wasted energy. |
| Upgrade to High-Efficiency Heating | Modern furnaces, boilers, or heat pumps convert more fuel to heat, reducing consumption. |
| Strategic Landscaping | Trees and shrubs act as windbreaks and allow passive solar gain, naturally insulating the home. |
Frequently Asked Questions About Eco-Friendly Home Design
The most impactful upgrade is generally improving insulation and air sealing. These measures directly prevent heat loss, reducing the load on your heating system significantly. An energy audit can pinpoint the most critical areas in your home for these improvements, often yielding the best return on investment.
Yes, absolutely. Homes with eco-friendly features and lower energy bills are increasingly attractive to potential buyers. Studies show that energy-efficient homes often sell faster and for a higher price, making eco-friendly upgrades a smart investment that enhances your property’s market value.
Yes, both federal and state governments in the United States offer various tax credits, rebates, and grants for homeowners who invest in energy-efficient upgrades, renewable energy systems, and other eco-friendly home improvements. It’s advisable to check local and national programs for eligibility and specific offerings.
Savings can be immediate, especially for simple measures like air sealing and adjusting thermostat settings. For larger investments like new insulation or high-efficiency heating systems, the payback period varies but typically ranges from a few years to a decade, after which savings continue indefinitely.
Not at all. While new constructions can integrate eco-friendly principles from the ground up, existing homes can undergo significant eco-friendly transformations through renovations and upgrades. Many impactful changes, such as insulation, air sealing, and smart thermostat installation, are highly suitable for retrofitting older properties to improve their efficiency.
Conclusion
Embracing eco-friendly home design is a powerful and practical strategy for homeowners looking to significantly reduce their winter energy bills, potentially saving up to 20% or more. From maximizing insulation and air sealing to integrating smart heating solutions and considering the impact of landscaping, every deliberate step contributes to a more efficient and sustainable living environment. Beyond the immediate financial benefits, these choices foster a healthier home and a reduced environmental footprint, aligning personal comfort with planetary responsibility. The transition is accessible and rewarding, ensuring that your home remains a warm, cost-effective sanctuary throughout the colder months and for many years to come.





